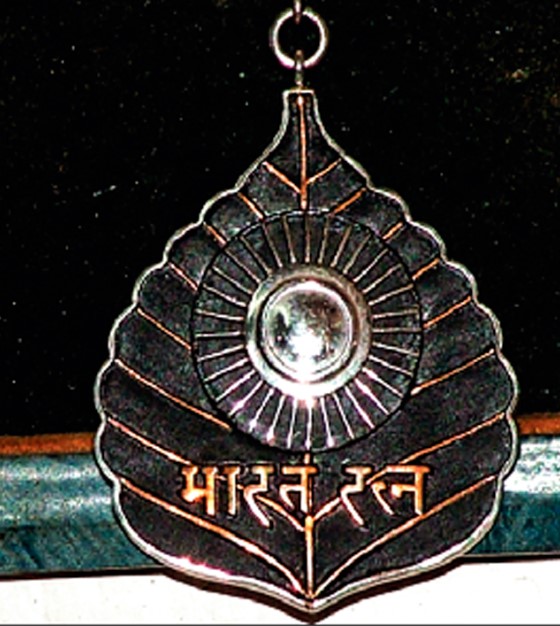
The Bharat Ratna (Hindi pronunciation: [b?a???t? r?t?n?]; Jewel of India)[1] is the highest civilian award of the Republic of India. Instituted on 2 January 1954, the award is conferred in recognition of "exceptional service/performance of the highest order", without distinction of race, occupation, position, or sex.[2][3][4] The award was originally limited to achievements in the arts, literature, science, and public services, but the government expanded the criteria to include "any field of human endeavour" in December 2011.[5] The recommendations for the Bharat Ratna are made by the Prime Minister to the President, with a maximum of three nominees being awarded per year. The recipients receive a Sanad (certificate) signed by the President and a peepal leaf-shaped medallion. There is no monetary grant associated with the award. Bharat Ratna recipients rank seventh in the Indian order of precedence.
The first recipients of the Bharat Ratna were: the last Governor-General of the Dominion of India and the former Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu – C. Rajagopalachari, second President and the first Vice President of India – Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan and Nobel Prize Laureate and Physicist C. V. Raman; who were honoured in 1954. Since then, the award has been bestowed upon 48 individuals, including 14 who were awarded posthumously. The original statutes did not provide for posthumous awards but were amended in January 1955 to permit them. Former Prime Minister Lal Bahadur Shastri became the first individual to be honoured posthumously. In 2014, cricketer Sachin Tendulkar, then aged 40, became the youngest recipient; while social reformer Dhondo Keshav Karve was awarded on his 100th birthday. The first singer to be awarded was M. S. Subbulakshmi and the first actor to be awarded was M. G. Ramachandran. Though usually conferred on India-born citizens, the Bharat Ratna has been awarded to one naturalized citizen – Mother Teresa, and to two non-Indians: Abdul Ghaffar Khan (born in British India and later citizen of Pakistan) and Nelson Mandela, born in and citizen of South Africa. On 25 January 2019, the government announced the award to social activist Nanaji Deshmukh (posthumously), singer-music director Bhupen Hazarika (posthumously) and to the former President of India, Pranab Mukherjee.
The Bharat Ratna, along with other personal civil honours, was briefly suspended from July 1977 to January 1980, during the change in the national government; and for a second time from August 1992 to December 1995, when several public-interest litigations challenged the constitutional validity of the awards. In 1992, the government's decision to confer the award posthumously on Subhas Chandra Bose was opposed by those who had refused to accept the fact of his death, including some members of his extended family. Following a 1997 Supreme Court decision, the press communiqué announcing Bose's award was cancelled; it is the only time when the award was announced but not conferred.
The bestowals of the posthumous awards of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel (1991) and Madan Mohan Malaviya (2015) drew criticism, because they died before the award was instituted.
On 2 January 1954, a press communique was released from the office of the secretary to the President announcing the creation of two civilian awards—Bharat Ratna, the highest civilian award, and the three-tier Padma Vibhushan, classified into "Pahela Warg" (Class I), "Dusra Warg" (Class II), and "Tisra Warg" (Class III), which rank below the Bharat Ratna. On 15 January 1955, the Padma Vibhushan was reclassified into three different awards; the Padma Vibhushan, the highest of the three, followed by the Padma Bhushan and the Padma Shri.
There is no formal provision that recipients of the Bharat Ratna should be Indian citizens. It has been awarded to a naturalised Indian citizen, Mother Teresa in 1980, and to two non-Indians, Abdul Ghaffar Khan of Pakistan in 1987 and the former South African president Nelson Mandela in 1990.[6] M. S. Subbulakshmi from Tamil Nadu became the first musician to receive the honour. Sachin Tendulkar, at the age of 40, became the youngest person and first sportsperson to receive the honour. In a special ceremony on 18 April 1958, Dhondo Keshav Karve was awarded on his 100th birthday.[non-tertiary source needed][a] As of 2019, the award has been conferred upon 48 people with 14 posthumous declarations.
The award was briefly suspended twice in its history. The first suspension occurred after Morarji Desai was sworn in as the fourth Prime Minister in 1977. His government withdrew all personal civil honours on 13 July 1977. The suspension was rescinded on 25 January 1980, after Indira Gandhi became the Prime Minister. The civilian awards were suspended again in mid-1992, when two Public-Interest Litigations were filed, one in the Kerala High Court and another in the Madhya Pradesh High Court, challenging the "constitutional validity" of the awards.[11] The awards were reintroduced by the Supreme Court in December 1995, following the conclusion of the litigation.